
- Derivative, Differentiable
- Partial Derivatives
- Gradients
- Chain Rule
1. Derivative, Differentiable

prime of f(x) is derivative. if derivatidve exists, f(x) is differentiable. Derivative f'(x) can be interpreted as the instantaneous rate of change of f(x) with respect to x.
All of following expressions are equal.
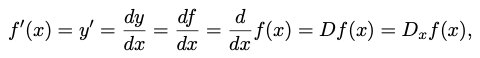
2. Partial Derivatives (편미분)

To calculate parital derivative of xi, we can simply treat x1,....,xi-1,xi+1,......,xn as constants and calculate the derivative of y with respect to xi.
3. Gradient
If input of function f : Rn → R is an n-dimensional vector x = [x1, x2, . . . , xn]⊤ and the output is a scalar. The gradient of the function f (x) with respect to x is a vector of n partial derivatives:


4. Chain Rule
To differentiate composite function, we use chain rule.
Ley's say y has variables u1, u2, . . . , um, where each differentiable function ui has variables x1, x2, . . . , xn. (composite function). Then chaing rule gives

'ComputerScience > Machine Learning' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Deep Learning - 1.6 Probability (0) | 2022.08.09 |
|---|---|
| Deep Learning - 1.5 Automatic Differentiation (0) | 2022.08.06 |
| Deep Learning - 1.3 Linear Algebra (0) | 2022.07.29 |
| Deep Learning - 1.2 Data Preprocessing (0) | 2022.07.28 |
| Deep Learning - 1.1 Data manipulation (0) | 2022.07.27 |



