1 Design Pattern
- 후에 유지보수를 쉽게하기 위해 일반화한 개발 패턴을 말한다.
- 코드의 중복을 줄이고 각 객체들이 단일 책임을 갖도록 하기 위한 방법론 모두가 디자인 패턴에 속한다.
- 일반적으로 올바른 프로그램의 구조 혹은 올바른 개발을 위한 가이드, 전략으로 활용된다.
- 재사용과 지속가능한 개발을 가능하게 하고 기술부채를 줄이는데 목적이 있다.
- 이번 장에서는 모바일 개발에 있어서 많이 사용되는 디자인 패턴들을 공부할 것 이다.
2 MVC
- Model - View - Controller
- 이전에 앱 개발에 있어서 널리 활용되던 디자인 패턴이다.

- 데이터와 UI를 controller가 중계하는 모델이다.
- 데이터의 변화 혹은 UI의 변화를 항상 controller가 인지하고 변화를 주도한다.
- controller에 부하가 쌓이기 쉽다. 즉 너무 많은 일을 감당하려고 하는 것이다.
3 MVVM
- Model - View - ViewModel
- 더 발전된, 널리 채택되어 사용되는 방식이다.
- 기존의 View Controller의 많은 역할을 View Model이라는 class로 위임하면서 view controller의 역할을 축소한다.
- class로 분리할 수 있다는 것은 그 역할을 분명히 표현할 수 있다는 뜻이고 이는 유지보수와 직결된다.

4 MVVM 적용하기

- 이전에 만들었던 앱에 새로운 디자인 패턴을 적용하여 refactoring 해보자
*BountyViewController 분해
| Model | View | ViewModel |
| Bounty Info - 현상금, 이름의 정보를 struct로 묶어서 객체로 관리하자 - View Model이 이 형식의 데이터들을 소유하고 있다. |
ListCell - 앞으로 ListCell은 정보를 ViewModel로 부터 받아와서 화면에 보여줄 것이다. |
- View Controller가 View와 Model에 직접 접근하면 안된다. - 따라서 그 역할을 대신 수행할 BountyViewModel이라는 클래스를 만들고 vc가 이 객체를 소유할 것이다. |
 |
 |
 |
import UIKit
struct BountyInfo {
let name: String
let bounty: Int
var image: UIImage? {
return UIImage(named: "\(name).jpg")
}
init(name: String, bounty: Int) {
self.name = name
self.bounty = bounty
}
}- 현상금, 이름을 struct로 묶어서 객체로 관리하자.
class BountyViewModel {
let bountyInfoList: [BountyInfo] = [
BountyInfo(name: "brook", bounty: 33000000),
BountyInfo(name: "chopper", bounty: 50),
BountyInfo(name: "franky", bounty: 44000000),
BountyInfo(name: "luffy", bounty: 300000000),
BountyInfo(name: "nami", bounty: 16000000),
BountyInfo(name: "robin", bounty: 80000000),
BountyInfo(name: "sanji", bounty: 77000000),
BountyInfo(name: "zoro", bounty: 120000000)
]
var sortedList: [BountyInfo] {
let sortedList = bountyInfoList.sorted { prev, next in
return prev.bounty > next.bounty
}
return sortedList
}
var numOfBountyInfoList: Int {
return bountyInfoList.count
}
func bountyInfo(at index: Int) -> BountyInfo {
return sortedList[index]
}
}- BountyViewModel은 bounty view controller가 사용할 데이터들을 가지고 있고 뷰컨트롤러와 view들은 BountyViewModel로 부터 데이터를 받아올 것이다. 이에 필요한 메서드들이 정의되어 있다.
import UIKit
class BountyViewController: UIViewController, UITableViewDataSource, UITableViewDelegate {
let viewModel = BountyViewModel()
func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, numberOfRowsInSection section: Int) -> Int {
return viewModel.numOfBountyInfoList
}
func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, cellForRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> UITableViewCell {
guard let cell = tableView.dequeueReusableCell(withIdentifier: "cell", for: indexPath) as? ListCell else {
return UITableViewCell()
}
let bountyInfo = viewModel.bountyInfo(at: indexPath.row)
cell.update(info: bountyInfo)
return cell
}
func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, didSelectRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) {
print("----> \(indexPath.row)")
performSegue(withIdentifier: "showDetail", sender: indexPath.row)
}
override func prepare(for segue: UIStoryboardSegue, sender: Any?) {
if segue.identifier == "showDetail" {
let vc = segue.destination as? DetailViewController
if let index = sender as? Int {
let bountyInfo = viewModel.bountyInfo(at: index)
vc?.viewModel.update(model: bountyInfo)
}
}
}
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
}
}
class ListCell: UITableViewCell {
@IBOutlet weak var imgView: UIImageView!
@IBOutlet weak var nameLabel: UILabel!
@IBOutlet weak var bountyLabel: UILabel!
func update(info: BountyInfo) {
imgView.image = info.image
nameLabel.text = info.name
bountyLabel.text = "\(info.bounty)"
}
}- bounty view controller는 bountyViewModel객체와 view(ListCell)를 소유하고 있다.
- view와 viewModel만이 소통이 이루어진다.
- ListCell을 독립된 파일로 분리해도 좋으나 이렇게 코드가 짧은 경우는 연관있는 파일에 모아 놓기도 한다.
*DetailViewController 분해
| Model | View | ViewModel |
| Bounty Info - 이전 스크린에서 클릭한 데이터를 viewModel이 소유하고 있는 model을 통해 넘겨받을 것이다. |
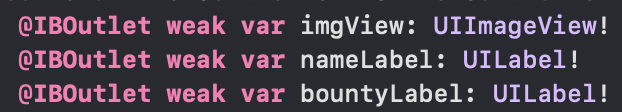
imgView, nameLabel, bountyLabel | - DetailViewModel이 DetailVeiwController의 역할 일부를 대신할 것이다. - model을 가지고 view와 소통하기 위한 메서드를 가지고 있다. |
 |
 |
 |
import UIKit
class DetailViewModel {
var bountyInfo: BountyInfo?
func update(model: BountyInfo?) {
bountyInfo = model
}
}import UIKit
class DetailViewController: UIViewController {
@IBOutlet weak var imgView: UIImageView!
@IBOutlet weak var nameLabel: UILabel!
@IBOutlet weak var bountyLabel: UILabel!
let viewModel = DetailViewModel()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
updateUI()
}
func updateUI() {
if let bountyInfo = viewModel.bountyInfo {
imgView.image = bountyInfo.image
nameLabel.text = bountyInfo.name
bountyLabel.text = "\(bountyInfo.bounty)"
}
}
@IBAction func close(_ sender: Any) {
dismiss(animated: true, completion: nil)
}
}- 이전 스크린에서 클릭한 bountyInfo를 veiwModel을 통해 넘겨 받았다.
- DetailViewController가 DetailViewModel을 가지고 있다.
- 이전에는 view controller가 모든 역할을 수행했지만 새로운 디자인 패턴을 적용하고 나서는 역할이 쪼개진 것을 알 수 있다.
- 데이터(model)를 가지고 view와 소통하는 역할은 viewModel이 수행한다.
- view controller라는 곳에서 view와 viewModel이 서로의 소통한다.
'ComputerScience > ios App(Storyboard)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| ios - 17 Animation with contraints (0) | 2021.08.03 |
|---|---|
| ios - 16 CollectionView (0) | 2021.08.03 |
| ios - 14 Segue (0) | 2021.07.28 |
| ios - 13 Custom Cell (0) | 2021.07.28 |
| ios - 12 Table View, Table View Cell (0) | 2021.07.25 |



